Effects of different Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein dosage on visual function in the Dark Agouti rat model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Young Investigator
Valerio Castoldi
Institute of Experimental Neurology (INSPE), San Raffaele Scientific Institute
62
Milan, Italy
Abstract
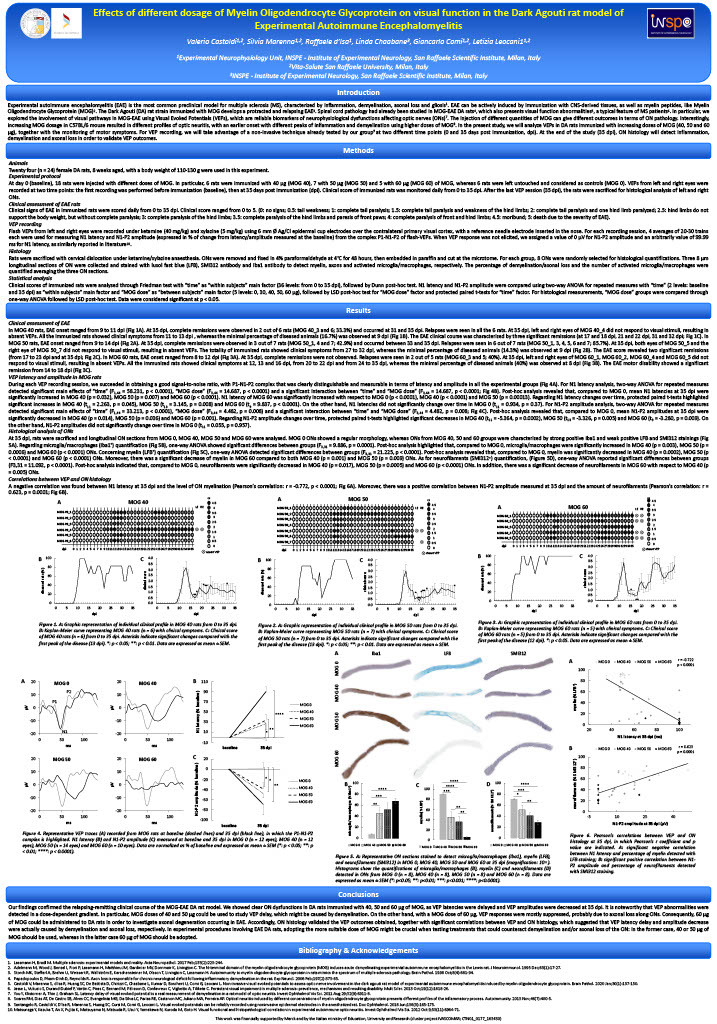
Dark-Agouti rats were immunized with increasing doses of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG) to develop Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE), a preclinical model of multiple sclerosis (MS). Typical EAE motor impairments were daily assessed and non-invasive Visual Evoked Potentials (VEPs) were recorded at baseline and five weeks after immunization, with final histopathology of optic nerves (ONs).
Immunized rats exhibited a relapsing-remitting clinical course. Both VEP and histological abnormalities were detected in a MOG dose-dependent gradient. Increasing MOG dosage affected visual function in EAE, which could be monitored with VEP recording to assess demyelination and axonal loss along ONs.
Effects of different Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein dosage on visual function in the Dark Agouti rat model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Valerio Castoldi,a, Silvia Marenna,a, Raffaele d’Isa,a, Linda Chaabane,a, Giancarlo Comia,b, Letizia Leocania,b
a Institute of Experimental Neurology (INSPE), San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy
b Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Milan, Italy
iframe width="100%" height="360" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/9nr44Pw5eqc" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture"